RaySi - Formulation & Coumpounding Company
Formulation of room temperature vulcanizing silicone elastomers, RTV-2 type by addition (rubbers or gels).
which are used in sealing, potting, encapsulation and coating in many industrial contexts, such as:
- Automotive
- Electronics
- Home appliances
- E-Mobility
- Electrical engineering
- Lighting
- Molding and modeling
- Thermo-hydraulics
- Construction
- Solar energy/photovoltaic
Products
Gels
Ray Si GELs are available in both standard and custom formulations.
We formulate and produce a wide range of products that differ in terms of cross-linking times, softness and color.
Two-component, FAST-CURING GELS, mixing ratio 1:20

Two-component, FAST-CURING GELS, mixing ratio 1:1
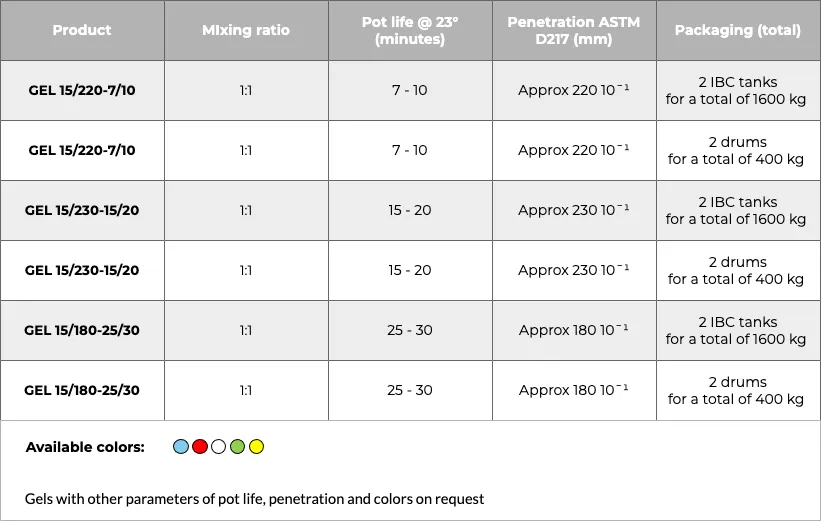
Two-component, SLOW-CURING GELS, mixing ratio 1:1
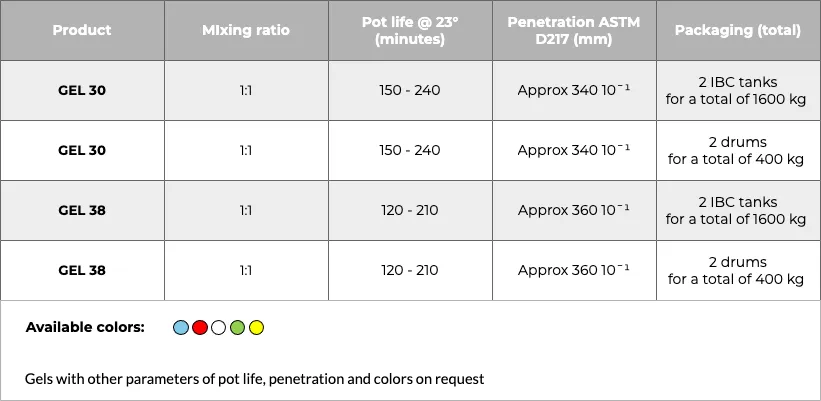
Rubbers
Ray Si rubbers are available in 2 variants, with high softness and with a medium Shore A hardness.
SOFT two-component RUBBERS with FAST cross-linking mixing ratio 1:1

HARD two-component RUBBERS with FAST cross-linking mixing ratio 1:1

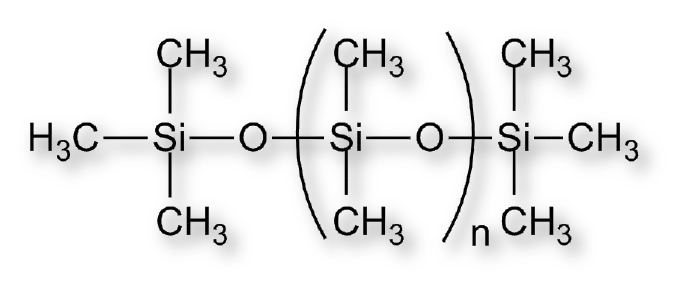
Formulations
RTV-2 silicone rubber and gel formulations are composed of two pourable, spreadable or kneadable parts that vulcanize after mixing at room temperature forming a material with different elasticity ranges. In addition to polysiloxane, the pourable parts generally contain:
CROSS-LINKING AGENTS
That is, hardeners (generally peroxides, silanes or polysiloxanes containing SiH) that allow the rubber to vulcanize
FILLER/FILLERS
Fillers are necessary to reinforce the silicone elastic network.
ADDITIVES
Contrary to other elastomers, the addition of additives is not fundamental as the essential properties are already determined by the polysiloxane itself but by way of example the formulation can include: catalysts, thermal stabilizers, adhesion promoters, rheological modifiers.
DYES
Silicone rubber is generally transparent or opaque but can be colored according to application needs.
Components
RTV-2 silicones are made up of two components that can be mixed in different weight ratios, depending on the type of formulation.
COMPONENT A contains the polymer and the catalyst.
COMPONENT B contains the polymer and the cross-linker.
When components A and B are mixed, the mixture immediately begins to polymerize to form the elastomer.
Polymerization is characterized by an increase in viscosity that causes a reduction in fluidity and a decrease in plasticity.
The term POTLIFE indicates the maximum workability time of the mixture, resulting in doubling of the initial viscosity.
The material must be used (poured/mixed) before the potlife has elapsed.
The VULCANIZATION time indicates the time within which the polymer will no longer be sticky, but the final properties, however, are usually achieved after a few hours or even days.
RTV-2 silicone elastomers typically have a potlife range of 5 to 45 minutes and take 15 to 90 minutes to cure.
Potlife and cure/vulcanization time can be adjusted by selecting a “slow” or “fast” curing agent and varying the mixing ratio.
The greater the amount of curing agent used, the shorter the curing time will be.
Recommendations:
- With a low amount of curing agent (component B), the cure will be unsaturated and the rubber will be soft or even tacky and with low mechanical strength.
- With a high amount of curing agent, the resulting elastomer will have decreased release properties, increased hardness, reduced elasticity and high possibility of embrittlement.
- The rate of cure can be slightly accelerated by increasing the temperature. However, heating should not exceed 80 °C before complete cure, otherwise the silicone rubber may be destroyed. At temperatures above 80 °C, the cross-linking reaction is reversed and the product will be sticky or will return to a soft state.
General properties of RTV silicone rubber and gels
- Exceptional long-term thermal resistance from -50 °C to +180 °C
- Low modulus of elasticity
- Coefficient of linear thermal expansion approx. 150∙10-6 – 300∙10-6 m/(m∙K)
- Excellent dielectric properties
- Constant properties over a wide range of temperatures and frequencies
- Electrically insulating
- High resistance to atmospheric agents, UV rays and radiation
- Flame retardant
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Workability
- Water-repellent surface combined with low moisture absorption
- Odorless and tasteless
- High chemical purity
- Chemical inertness and biocompatibility
- High gas permeability
- Density: from 0.96 up to over 3 g/cm³
- Hardness: 20 Shore 00 – 80 Shore A, or gel
- Tensile strength: 2 – 10 N/mm²
- Elongation at break: 100 – 900 %
- Tear strength (ASTM D 624): 5 – 30 N/mm
- Compression set (22 hours/175 °C) ≥ 5 %
Notes on the exposition of gels and rubbers to chemicals
Precautions for use
Caution: pour into clean and dry enclosures
Before opening and mixing the components, make sure that the enclosures are clean and dry, free from processing waste or dust or residues that can inhibit correct cross-linking. Latex, heavy metal salts, amines, sulfides and derivatives, epoxy resin catalysts can inhibit cross-linking.
Do not invert the caps/lids of the 2 components and close them at the end of use in case of multiple applications.
Caution: stains
The product stains and is difficult to remove if accidentally spilled on clothes and floors.
Cleaning stains on floors:
- If the product is spilled on the floor BEFORE CROSS-LINKING:
it is recommended to collect it with a rag, clean by rubbing well with normal floor cleaner (for domestic use, but strong type) and possibly finish the cleaning with a suitable chlorinated solvent, such as trichloroethylene. - If the PRODUCT spilled on the floor is ALREADY CROSS-LINKED: we suggest removing the gel with a spatula, then cleaning with normal floor cleaner (for domestic use, but of the strong type), and possibly finishing the cleaning with a rag or sponge, preferably hard and rough, soaked in a suitable chlorinated solvent, such as trichloroethylene.
- From experience, products based on trichloroethylene (trichlorethylene), when available on the market, are suitable for cleaning the product, but they must be used with due caution according to the supplier’s instructions.
Exposure to chemicals of the cross-linked product
Salt, salty water, etc: Have no adverse effect.
Sea water or chlorine environments (swimming pools etc): Have no adverse effect.
Inorganic acids in water solutions: Haven not visible effects.
Strong, pure acids or alkaline (not in solution): The exposition has to be avoided, especially at high temperature.
Alkaline solutions and vinegar: Could bring, after a long time of exposition, to a softening of the external surface.
Solutions of hydrocarbons in water: Could give, after a long exposition at quit hight temperatures, the hardering of the external surface of the products; of course, nothing happens for temporary expositions.
Strong and undiluted hydrocarbons (pure): Permanent immersion in strong and pure hydrocarbons has to be avoided.
Shelf life
ATTENTION: The prolonged exposure to temperatures ≥ 40° C is not recommended.
The product has unlimited shelf life, if it is stored in a suitable way, in the original closed packages.
For precautions we recommend the use within 5 years.


